By Laura Putnam, Compliance Content Manager, Global Trade Intelligence, Descartes

Russia's incursion into Ukraine on February 24, 2022, led to a series of comprehensive global sanctions, significantly increasing the complexity of trade compliance for businesses worldwide.
The geopolitical responses were striking, from the pursuit of assets owned by prominent Russian oligarchs, including Viktor Vekselberg, to the imposition of asset freezes on key figures like President Putin and Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov. These sanctions, affecting critical sectors such as oil and natural gas, underscore the widespread impact on Russia’s economy. For those in global trade, the withdrawal of over 1,000 brands from the Russian market highlighted the broader implications for businesses and the necessity for stringent sanctions screening measures in navigating this challenging compliance landscape.
In this article, we will take a look at the complexities of Russia sanctions, the importance of global sanctions screening, and how trade compliance software can help simplify efforts to adhere to the mounting regulations.
Key Takeaways
- Russia’s invasion of Ukraine triggered a wave of widespread sanctions and export controls that have significantly complicated the trade compliance landscape.
- These developments have also increased the difficulty in export classification for dual-use and military-use goods, with some controlled items like discrete chemicals not having HS codes and requiring exporters to provide their HS classification.
- With Russia Sanctions frequently growing in complexity and quantity, businesses must implement robust global sanctions screening measures to secure their operations.
- Automated sanctions screening software with export classification capabilities is crucial for identifying sanctioned / denied entities and ensuring that transactions comply with international sanctions programs.
- Descartes offers robust integrated denied party screening software that helps businesses streamline their global sanctions screening procedures, ensuring trade compliance.
Overview of the Extensive Russia Sanctions Programs
The wide-ranging effect of the sanctions implemented on Russia and Belarus is so expansive that it just stops short of an embargo. None of the countries participating in these sanctions want businesses within their borders to do business with Russia and Belarus and have made it a very challenging climate for those who continue to do it. The U.S., UK, and EU along with Australia, Canada, and Japan have collectively imposed over 16,500 Russia sanctions, making it the most sanctioned country to date.
These sanctions and export controls are designed to cripple Russia’s ability to continue to fight and finance its war against Ukraine. As such, none of the countries enforcing these restrictions want businesses, that fall under their jurisdiction, to engage in commerce with Russia and Belarus, creating a highly challenging business climate for those who persist.
There are different types of Russia sanctions imposed such as asset freezes, import bans, sectorial sanctions, Russian and Belarusian entities / individuals added to sanctioned / denied party lists, and export license requirements for dual-use goods, software, and technology along with luxury goods.
Recently, there has been an intensified focus on Russia sanctions evaders and third country supporters who are facilitating illicit trades. U.S. export control agencies are taking coordinated action to strengthen enforcement of Russia sanctions and curb diversion activities. We covered some of the efforts undertaken by the Bureau of Industry Security (BIS) and other regulators in an earlier article.
Complications with Exporting to Russia
To provide a picture of what the trade compliance landscape looks like for managing exports to Russia, here’s a look at the export controls that the U.S. put in place:
1. Export licensing requirement (including in-country transfers) for more than 600 categories of dual-use goods, software, or technology. License exceptions are very limited (e.g., some mass market items under 5A992 or 5D992).
2. Export license requirement for export, reexport or transfer (in country) to or within Russia of items subject to the export control classification number (ECCNs) listed in Section 746.5(a)(1)(i) or any of the items listed in Section 746.5 Supplement No. 2 to Part 746 of the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) (for certain deepwater oil-and-gas-related end uses), and for the export, reexport or transfer (in country) to or within Russia of such items (for certain Arctic offshore or shale formation oil-and-gas-related end uses).
3. Export license requirement for export, reexport or transfer (in country) to or within Russia of items listed in Supplement Nos. 4 and 6 to Part 746 of the EAR. Supplement No. 4 includes additional sector sanction items and Supplement No. 6 has the list of EAR99 items that are considered an extension of the Commodity Control List (CCL).
4. Export license required for exports, reexports and transfers to or within Russia of over 600 luxury goods listed in Section 746.5 Supplement No. 5 to Part 746 of the EAR, as well as to designated Russian oligarchs, or other persons, regardless of their location.
5. As of February 23, 2024, BIS has placed over 900 parties on the Entity List linked to the Ukraine invasion and has designated nearly 400 Russian and Belarusian entities/individuals as Military End Users (MEUs) that are now on the BIS Entity List.
6. Also, on February 23, 2024, the Common High Priority List (same for EU, UK and Japan) composed of fifty items subject to stringent export controls designed to restrict Russia’s access to technologies and other critical items deemed necessary for its war arsenal.
A Strategic Approach is Required
If you are still doing business in Russia, what’s your go-forward export compliance strategy? The Russia sanctions and export controls discussed earlier significantly restrict the technology, commodities, and software that can be exported to or transit through Russia and Belarus. Additionally, they limit the eligibility of certain entities (individuals, companies, vessels) that can receive items from the U.S. or any of the allied countries. To operate with full compliance, the nature and magnitude of Russia sanctions requires different types of screening and tracking, depending on the types of goods and/or services your company provides to Russia or Belarus.
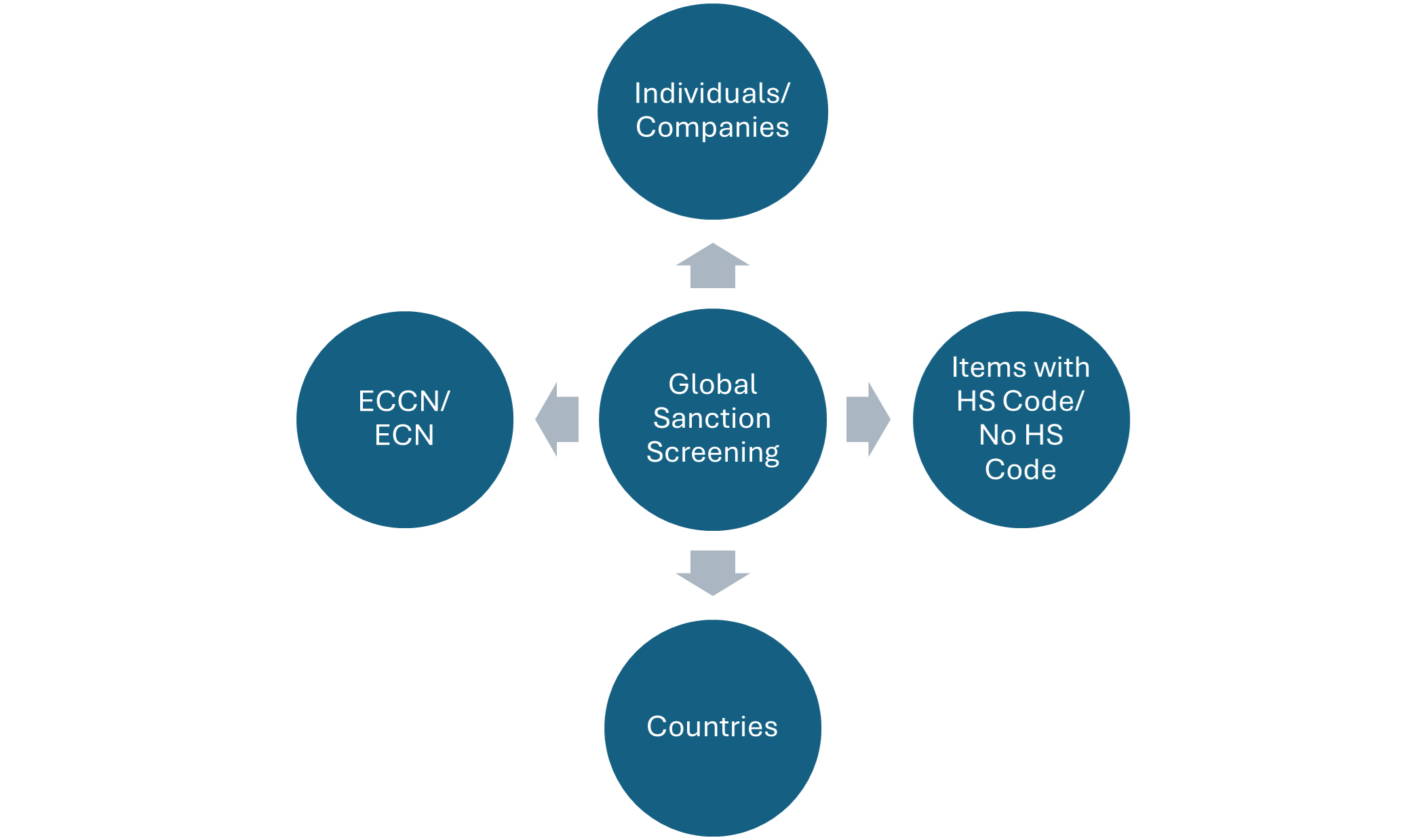
Figure 1: Effective global sanctions screening requires checking all aspects of a transaction
To better navigate the challenges of doing business in Russia and Belarus while maintaining compliance with international regulations, exporters should undertake these steps.
1. Implement a robust export compliance program that leverages technology to perform thorough due diligence, regular audits, and continuous monitoring of transactions and partners.
A. With advanced global sanctions screening software, these lists of sanctions require different types of screening and tracking, depending on the types of goods and/or services your company provides to Russia or Belarus. Trade compliance professionals can easily handle the ever-growing lists of individuals and entities added to the sanctioned / denied party lists. It doesn’t matter if there are 10 additions or 1,000 additions, they are automatically picked up via updated denied party lists in the sanctions screening software, which will alert you if there is a business partner that has been added to these lists.
2. Verify whether an export license is required for the goods, technology, or services being exported to Russia or Belarus, especially for dual-use items. Determine the proper export classification for the item and then review the appropriate EAR supplement.
3. Perform a check to see if your item falls out of the scope of product coverage. For example, the EU uses the prefix “ex” before an HS code to denote that the scope of product coverage classified under that HS code is limited. There are hundreds of these HS codes in the EU Russia sanctions in the category of luxury goods under Annex XVIII. For example, under the EU HS heading 9013 for lasers, a red dot sight is called out as a luxury good subject to the Russia sanctions. All other telescopic sights for fitting to arms or for periscopes are exempted from it.
4. Maintain detailed records of all transactions, Russia sanctions screening activities, export license processes, and trade compliance efforts to demonstrate due diligence.
The Case for Export Classification Solutions
Dual-use goods items have an ECCN assigned to them. If any of your company’s items fall on this list, you would have to check to see if an export license is required for any of them and if an export license exception applies. Once again, most trade compliance professionals would have a list of export control classification numbers or some sort of record-keeping system that they could use to cross reference and validate to see if additional license determinations have to be made.
The most notable aspect is the list of over 100 items in Supplement No. 6, which includes discrete chemicals, biologics, fentanyl and its precursors, and related equipment. There are no HS classifications provided for any of these goods, so it is up to the exporter to classify them accurately. Chemicals are amongst the hardest items to classify and can require a consultation with a staff chemist to determine the correct HS classification. At a recent export compliance conference, there was an advanced chemical classification course, highlighting the complex decision trees required for accurate classification. If your organization lacks in-house expertise, you may need to hire a specialist or pay an expert to classify these items correctly.
The monitoring of these items is a challenge because changes are numerous and expansive. These lists of items are subject to modification with each country’s amendment to its sanctions’ regulations. There are frequent additions to restricted lists and deletions can occur as well. For the recent U.S. BIS update on June 18, 2024, a total of 539 items were added to Supplemental No. 4 and Supplemental No. 6 to 15 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 746. In the case of the EU’s 14th package of Russia sanctions on June 24, 2024, it further expanded sectorial restrictions with one annex deleted, five annexes added, three annexes amended, and five annexes replaced. An export classification software solution will help streamline this process, with automated updates that keep up with any new additions, deletions, and other regulatory changes.
Another area where export classification and export license solutions shine is with handling different languages and writing conventions. When managing a sanctions compliance program on a global scale with multiple subsidiaries in various countries, language barriers often compound the complexity of screening and classifying restricted items. Translations in English are not always available for some countries like Japan. Only a partial translation is typically available for South Korea.
If you don’t have employees overseas to assist with translating regulatory data sets in unfamiliar languages, you will also have to look outside your company for the resources to ensure due diligence in complying with the country’s particular set of sanctions. The Common High Priority List is the only one that is the same across the four countries implementing it.
How Descartes Can Help
The most effective and efficient way to screen against the massive wave of sanctions against Russia, Belarus, and other nations is with robust global sanctions screening software solutions, such as those offered by Descartes. These sanctions screening solutions are effective because they can integrate with your ERP or other business systems and have the capability to constantly rescreen your entire supply chain against sanctions programs and instantly alert you of a potential match. This is especially important because a partner cleared to do business today might have a restricted compliance status tomorrow.
To meet evolving compliance requirements, Descartes adds new entities to its screening lists as soon as government and other official sources update theirs. List content related to international sanctions programs is updated within our application on an ongoing basis, and any additions will be made promptly to help keep our customers in compliance with sanctions and embargo programs.
Descartes is a provider of an industry-leading suite of denied party screening, global trade management content, 3rd party risk management solutions, as well as sanctions screening content for leading business systems.
Descartes Visual Compliance and Descartes MK solutions are flexible and modular, allowing organizations to pick the specific and exact functionality and content they need for their particular compliance needs and scale up later as and when necessary.
If you would like to take a closer look at our sanctions screening technology, you can simply contact us or request a demo. Find out what our customers are saying about Descartes Denied Party Screening on G2 – an online third-party business software review platform.
